Understanding 158.63.258.200: A Deep Dive into IP Addressing
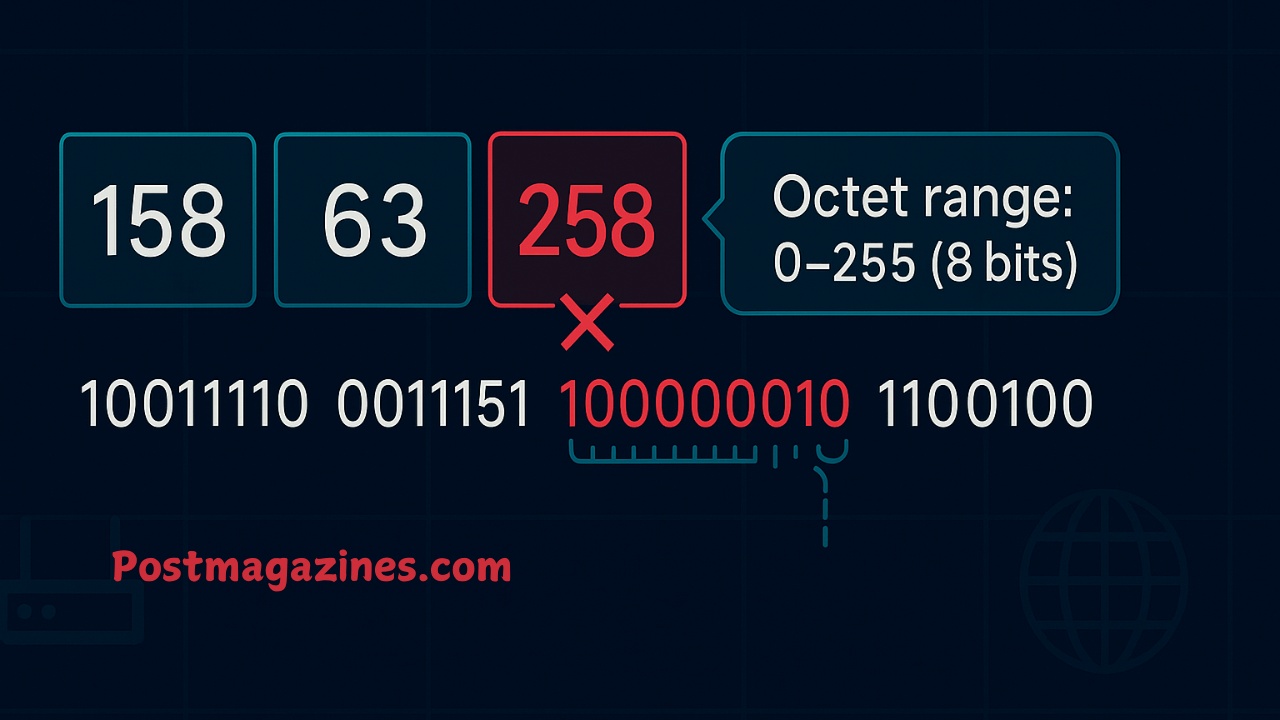
The 158.63.258.200 appears like a typical IPv4 address, yet it raises crucial questions about how IP addresses work, their structure, and validity. While it seems familiar, a closer examination reveals that 158.63.258.200 is not a valid IPv4 address, as its third octet, “258”, falls outside the allowed range of 0–255. This article will explore the meaning behind 158.63.258.200, how IP addressing works, why the string is invalid, and what lessons can be learned from such examples.
What Is 158.63.258.200?
At first glance, 158.63.258.200 resembles a standard IPv4 address, which consists of four numerical segments (octets) separated by dots. The value of each octet may vary from 0 to 255. For example:
- A valid IP: 192.168.0.1
- An invalid IP: 300.50.10.2 (since “300” exceeds 255)
The IP address 158.63.258.200 is invalid because its third octet, “258”, exceeds 255. Despite this, many websites reference it, often in explanations about networking or IP formats.
Why 158.63.258.200 Is Invalid
To understand the invalidity of 158.63.258.200, we must review how IPv4 addresses are structured:
- Four octets – Each part separated by dots.
- Range limitation – Every octet must be between 0 and 255.
- Binary representation – Each octet represents 8 bits, making IPv4 addresses 32 bits long.
Since “258” cannot be represented within 8 bits, 158.63.258.200 cannot function as a real IP address.
Common Uses of 158.63.258.200 Online
Even though 158.63.258.200 is not technically usable, it often appears in the following contexts:
- Illustrations in networking blogs – Some articles use it to demonstrate IP formatting.
- SEO content – The keyword is sometimes placed in posts as clickbait or filler for traffic.
- Educational errors – It may appear in training material when authors want to highlight what a “wrong IP” looks like.
Valid IP Alternatives to 158.63.258.200
If someone intended 158.63.258.200 to represent a real IP, they might have meant something like:
- 158.63.25.200
- 158.63.128.200
- 158.63.200.200
These are valid because all octets stay within the 0–255 limit.
How to Test Whether an IP Like 158.63.258.200 Works
If you encounter something like 158.63.258.200, you can check its validity in several ways:
- Syntax check – Confirm all octets are between 0 and 255.
- Ping or traceroute – If the IP address is valid, you can try to reach it from a terminal.
- WHOIS lookup – Valid IP addresses are usually associated with an ISP, company, or hosting provider.
In the case of 158.63.258.200, the check fails immediately at the syntax stage.
Lessons from 158.63.258.200 in Networking
The keyword 158.63.258.200 highlights important lessons in networking:
- Data validation matters – Systems must reject invalid IPs to avoid misrouting.
- Human errors happen – A small typo, like writing 258 instead of 25, can break connectivity.
- Education opportunities – Invalid examples help learners understand constraints of IP addressing.
IPv4 vs IPv6: Where Does 158.63.258.200 Fit?
The existence of invalid strings like 158.63.258.200 also shows why the internet is moving toward IPv6:
- IPv4 limitation – Only about 4.3 billion addresses are possible.
- IPv6 expansion – Provides 340 undecillion possible addresses.
- Error reduction – IPv6 has stricter formatting, making it harder to confuse numbers.
Still, even in IPv6, values are bound by specific hexadecimal ranges, so incorrect entries remain possible.
The SEO Angle of 158.63.258.200
Many SEO-driven websites use 158.63.258.200 as a keyword. Why?
- Unique yet rare – It appears to be a technical IP, but it is uncommon enough to rank in searches.
- Educational value – It aligns well with tutorials on the distinction between valid and invalid IP addresses.
- Click curiosity – People who see “158.63.258.200” may wonder if it hides a deeper meaning.
As a result, even an invalid IP can attract online attention.
Misconceptions About 158.63.258.200
Some misconceptions that appear online include:
- It’s a real server IP – False. No real device can use 158.63.258.200.
- It’s reserved – No, it’s simply invalid, not part of private or special ranges.
- It’s a hidden code – Some blogs spin conspiracy-like interpretations, but in reality, it’s just an invalid string of characters.
Educational Value of 158.63.258.200
While invalid, 158.63.258.200 has value in teaching:
- For IT students – Shows what an error in IP entry looks like.
- For programmers – Reminds developers to validate user input.
- For digital literacy – Demonstrates how online misinformation spreads around technical-sounding terms.
Conclusion: The Truth About 158.63.258.200
In summary, 158.63.258.200 appears to be an IPv4 address but is invalid because the number “258” exceeds the allowed range. Despite this, the keyword is often used across websites, particularly in educational, SEO, or illustrative contexts.
FAQS
Q1: Why is 158.63.258.200 considered an invalid IP address?
A: IPv4 addresses are made up of four octets, each ranging from 0 to 255. The third octet in 158.63.258.200 is “258,” which exceeds the maximum value of 255, making the address invalid.
Q2: Can an IP address ever contain a number higher than 255?
A: No. In IPv4, every octet represents 8 bits, which can only express values from 0 to 255. Any number outside this range—such as 258—cannot be described in standard IPv4 addressing.
Q3: Why does 158.63.258.200 appear on websites even though it is not real?
A: It is often used in educational content, SEO examples, or networking tutorials to demonstrate what an invalid IP address looks like. Some websites also use it as a keyword to attract technical readers.
Q4: What is the correct way to check if an IP address like 158.63.258.200 is valid?
A: You can perform a simple syntax check to ensure each octet is between 0 and 255. Tools like WHOIS lookup, ping, or traceroute can verify connectivity only if the IP is already syntactically valid.
Q5: Does IPv6 solve problems like the invalid 158.63.258.200 address?
A: IPv6 provides a vastly larger address space and different formatting, reducing the chances of running out of addresses. However, even in IPv6, entries must still adhere to specific formatting rules to be considered valid.
You May Also Read: Znxnz: The Emerging Digital Concept You Need to Know